- All
- Product Name
- Product Keyword
- Product Model
- Product Summary
- Product Description
- Multi Field Search
Water is essential for life, but how do we ensure its quality and safety? With rising demands for clean water, monitoring water quality is more important than ever.
In this article, we will explore the different types of water sensors, including the versatile multiparameter sensors, and their applications across various industries. You'll learn how these sensors help monitor and manage water quality and levels efficiently.
Water sensors are devices designed to measure specific parameters of water, such as its quality, level, temperature, or chemical composition. They are used in a variety of sectors to ensure water meets the required safety standards for its intended use.
These sensors play a crucial role in industries such as municipal water treatment, agriculture, aquaculture, environmental monitoring, and industrial processes. By providing real-time data, water sensors help ensure that water remains safe for consumption, use in production processes, and does not cause harm to the environment.
Water sensors serve several functions, including:
● Detection of contaminants: Sensors can detect pollutants, bacteria, heavy metals, or other harmful substances in water.
● Monitoring water levels: Water sensors help measure the height of water in reservoirs, tanks, or natural water bodies, ensuring efficient resource management.
● Ensuring regulatory compliance: Water sensors help industries meet water quality standards set by regulatory bodies, preventing violations and associated fines.
These functions are essential for maintaining the safety and quality of water, whether for drinking, irrigation, industrial processes, or environmental protection.
Water sensors can be broadly categorized into two main types: water quality sensors and water level sensors. Each category includes a variety of specific sensors designed to measure different water parameters.
Water quality sensors are designed to monitor the chemical, physical, and biological characteristics of water. These sensors ensure that water meets the necessary quality standards for consumption, use, and environmental sustainability.
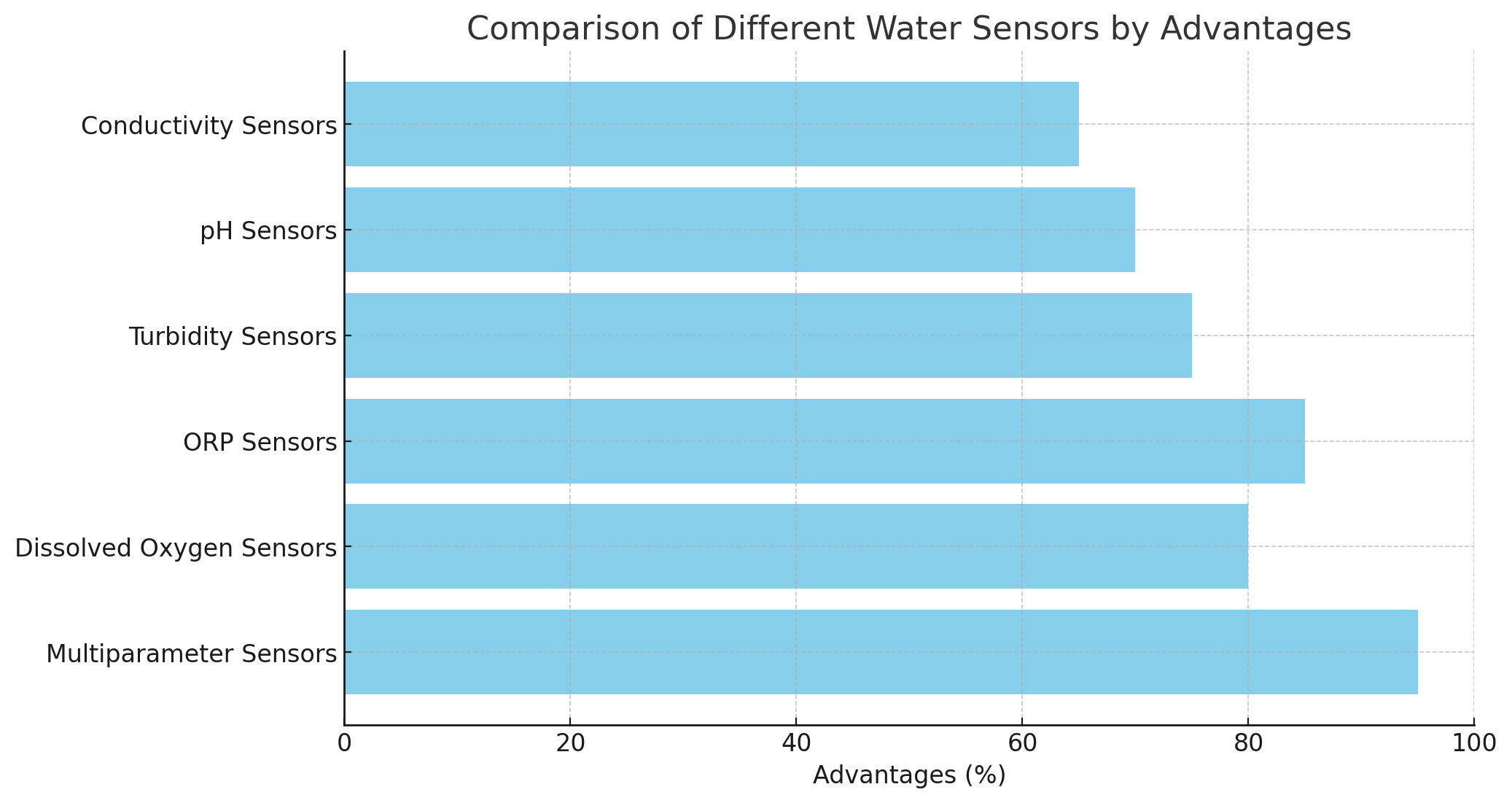
Multiparameter sensors are an innovative solution for comprehensive water quality monitoring. Unlike traditional sensors that measure a single parameter, multiparameter sensors can monitor several parameters simultaneously, such as pH, turbidity, dissolved oxygen (DO), and oxidation-reduction potential (ORP).
Benefits of Multiparameter Sensors:
● Efficiency: Multiparameter sensors reduce the need for multiple instruments, simplifying monitoring tasks.
● Comprehensive data: They provide a holistic view of water quality by measuring multiple variables at once.
● Cost-effective: By consolidating various sensors into one unit, multiparameter sensors reduce both equipment and maintenance costs.
Multiparameter sensors are increasingly used in applications like municipal water treatment, wastewater monitoring, aquaculture, and industrial processes. They help streamline water quality management, providing critical data that supports decision-making and ensures compliance with water quality regulations.
Dissolved oxygen sensors measure the amount of oxygen dissolved in water, which is essential for the survival of aquatic life. Low oxygen levels can be harmful to fish and other aquatic organisms, making DO monitoring a key aspect of environmental and industrial water quality control.
DO sensors are widely used in:
● Environmental monitoring: To ensure water bodies have sufficient oxygen levels for aquatic life.
● Wastewater treatment: To control aeration processes and optimize the efficiency of biological treatment systems.
● Aquaculture: To maintain healthy oxygen levels in fish farms.
Oxidation-reduction potential (ORP) sensors measure the water's ability to oxidize or reduce substances, indicating its chemical quality. ORP is a critical factor in water treatment, where it helps monitor the effectiveness of disinfection processes. A high ORP reading indicates strong oxidizing potential, which is important for breaking down pollutants.
ORP sensors are used in:
● Water treatment: To monitor the effectiveness of disinfectants like chlorine.
● Swimming pools: To maintain safe water quality by managing disinfection.
● Industrial systems: To control water quality in processes that require precise chemical management.
Turbidity sensors measure the cloudiness or haziness of water caused by suspended particles. High turbidity can indicate the presence of pollutants, microorganisms, or other contaminants. Monitoring turbidity is essential for water treatment and environmental protection.
These sensors are commonly used in:
● Water treatment plants: To ensure water clarity before distribution.
● Environmental monitoring: To assess the health of rivers, lakes, and oceans.
● Wastewater treatment: To monitor the efficiency of treatment processes.
pH sensors measure the acidity or alkalinity of water, a critical parameter that affects chemical reactions and the behavior of pollutants. Water with a low or high pH can cause corrosion, damage equipment, or harm aquatic life.
Applications of pH sensors include:
● Water treatment: To adjust chemical dosages for neutralizing acidic or alkaline water.
● Aquaculture: To maintain optimal pH levels for fish health.
● Industrial applications: To monitor and adjust water used in manufacturing processes.
Conductivity sensors measure the ability of water to conduct electricity, which is directly related to the concentration of dissolved salts (ions). Salinity sensors measure the amount of dissolved salts in water, which is crucial for various industrial and environmental applications.
These sensors are commonly used in:
● Marine environments: To monitor salinity levels in oceans and estuaries.
● Agriculture: To assess the suitability of irrigation water.
● Industrial processes: To ensure water quality in cooling and heating systems.
Water level sensors are used to measure the height of water in tanks, reservoirs, or natural bodies of water. These sensors are essential for managing water resources, ensuring safety, and preventing overflows or dry pumps.
Radar liquid level sensors use microwave radar technology to measure the distance between the sensor and the surface of the liquid. These sensors provide accurate measurements even in challenging environments with high temperatures, pressure, or corrosive liquids.
Radar level sensors are commonly used in:
● Water treatment plants: To monitor water levels in tanks and reservoirs.
● Industrial tanks: For liquid storage management.
● Environmental monitoring: To measure water levels in rivers, lakes, and wetlands.
Ultrasonic level sensors use sound waves to measure the distance between the sensor and the liquid surface. The time it takes for the sound wave to travel to the surface and back is used to calculate the liquid level.
These sensors are ideal for:
● Water tanks: For continuous monitoring of liquid levels.
● Wastewater systems: To measure levels and control treatment processes.
● Reservoirs: To ensure proper water storage management.
Float switches are mechanical devices that use a floating object to detect the water level. As the water level rises or falls, the float activates a switch. Capacitance sensors detect changes in capacitance caused by the presence of water.
Both sensors are used in:
● Residential applications: For monitoring water levels in home water tanks.
● Industrial applications: For ensuring safe water levels in manufacturing processes and cooling systems.
Hydrostatic level sensors measure water levels based on the pressure exerted by the liquid. These sensors are typically used in clean or slightly contaminated water, such as in reservoirs, rivers, and lakes.
Applications of hydrostatic sensors include:
● Environmental monitoring: To measure water levels in natural bodies of water.
● Industrial applications: To monitor liquid levels in tanks and storage units.
Each type of water sensor offers unique advantages, but they also have some limitations depending on the application.
Pros:
● Provide a comprehensive view of water quality by measuring multiple parameters simultaneously.
● Cost-effective by consolidating multiple sensors into one unit.
● Ideal for industries where real-time monitoring of several variables is required.
Cons:
● May require more frequent maintenance and calibration to ensure accuracy.
● More complex systems may lead to higher initial costs.
Pros:
● Provide critical data for maintaining aquatic life and effective water treatment.
● Highly reliable for monitoring oxygen levels and chemical reactions in water.
Cons:
● Can be affected by changes in temperature and contamination, which may require recalibration.
● Electrochemical DO sensors require regular maintenance, such as membrane replacements.
Pros:
● Provide accurate non-contact measurements, ideal for hazardous or hard-to-reach areas.
● High durability in extreme conditions (e.g., high pressure, temperature, or corrosive environments).
Cons:
● Radar sensors may experience interference from environmental factors, affecting accuracy.
● Ultrasonic sensors may be affected by surface foam or temperature variations.
Water sensors are widely used across several industries to ensure safe water usage and compliance with regulations.
Water sensors are essential in municipal water treatment plants for ensuring that drinking water meets health standards. They monitor water quality at various stages, from source to distribution, ensuring contaminants like bacteria, heavy metals, and chemicals are removed.
Industries use water sensors in their processes to maintain water quality for cooling, heating, and production. Sensors help optimize water usage, prevent equipment damage, and ensure the final products meet required standards.
In agriculture, water sensors are used in irrigation systems to monitor soil moisture and water quality. In aquaculture, they ensure the health of aquatic organisms by maintaining optimal water conditions, such as dissolved oxygen levels.
Water sensors help monitor rivers, lakes, and oceans, detecting pollutants and assessing ecosystem health. They play a vital role in tracking pollution, managing resources, and supporting sustainable practices in environmental conservation.
Choosing the right water sensor depends on several factors:
● Sensor type: Whether you need a multiparameter sensor or a specific sensor like pH or turbidity depends on the application.
● Environmental conditions: Consider the environment in which the sensor will be deployed, such as temperature, pressure, and the presence of contaminants.
● Accuracy and reliability: Choose sensors with the required accuracy for your application to ensure reliable monitoring.
● Installation requirements: Consider the ease of installation and whether the sensor will need to be calibrated frequently.
Water sensors are essential for ensuring water quality and safety across industries. They provide vital data for managing water resources in areas like municipal treatment, industrial use, and environmental monitoring. Multiparameter sensors, especially, offer a comprehensive, cost-effective solution to monitor multiple water quality parameters at once. When choosing a water sensor, it's crucial to match the sensor to your specific needs to ensure accurate, reliable, and real-time data. For those seeking advanced water sensor solutions, Leadmed Technology offers products that deliver exceptional value through precise and efficient monitoring capabilities.
A: Water sensors are used to monitor and measure water quality and levels in various industries, including municipal water treatment, agriculture, and environmental monitoring. They help detect contaminants and ensure water meets safety standards.
A: Multiparameter sensors are devices that can measure multiple water quality parameters simultaneously, such as pH, turbidity, dissolved oxygen, and ORP. This provides a comprehensive and cost-effective solution for water quality monitoring.
A: Multiparameter sensors use different sensors in a single unit to measure various water quality parameters. This allows for simultaneous data collection, making them efficient and reliable for real-time water monitoring.
A: Choosing multiparameter sensors allows for more efficient water quality monitoring as they can measure several key parameters at once, saving time and cost while providing comprehensive data.
A: Multiparameter sensors provide a broader view of water quality by measuring multiple parameters, reducing the need for multiple devices and simplifying data management. This can lead to more accurate assessments of water conditions.